Managing PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) can feel like a constant balancing act. Between insulin resistance, weight fluctuations, and hormonal imbalances, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. But what if there was a way to support your body’s needs and reduce some of these symptoms? That’s where the ketogenic diet comes in.
The keto diet, which is low in carbs and rich in healthy fats, has become an increasingly popular approach for managing PCOS. By stabilizing blood sugar levels, improving insulin sensitivity, and promoting weight loss, it offers hope for women struggling to manage these challenges.
In this article, we’ll explore how the ketogenic diet might help women with PCOS feel better and improve their health outcomes. Whether you’re curious about how it works, or you’re considering trying it yourself, we’ll break it down into practical, evidence-based insights so you can make an informed choice.
Contents
- 1 Why Keto Can Help Women with PCOS (Beyond Weight Loss)
- 2 How to Tailor Your Keto Macros for PCOS
- 3 Sample 7-Day PCOS Keto Meal Plan That Won’t Feel Restrictive + Free PDF Download
- 4 Hidden Traps: Common Keto Mistakes That Can Worsen PCOS Symptoms
- 5 Lifestyle Tweaks to Boost Keto Results for PCOS
- 6 Tracking Your Progress Safely: What to Measure and When
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 References
Why Keto Can Help Women with PCOS (Beyond Weight Loss)
If you have PCOS, you know it’s not just about losing weight. Hormones, energy swings, cravings, and blood sugar all affect your daily life — and the right eating plan can make a huge difference. The ketogenic diet, when tailored for PCOS, may do more than help shed pounds. It can support insulin sensitivity, hormone balance, and even mental clarity, giving you tools to feel more in control of your body.
Improves Insulin Sensitivity
Insulin resistance is a core challenge for many women with PCOS. When your body struggles to use insulin effectively, blood sugar spikes can trigger cravings, energy crashes, and fat storage, particularly around the abdomen.
A low-carb, high-fat keto approach can help stabilize blood sugar, reduce insulin surges, and improve how your body responds to this crucial hormone. Studies in peer-reviewed journals show that low-carb diets can enhance insulin sensitivity in women with PCOS, supporting weight management and overall metabolic health.
Supports Hormonal Balance
High insulin can push the ovaries to produce extra androgens, which may cause acne, excessive hair growth, and irregular cycles. By reducing insulin through a keto-style eating pattern, you may help rebalance hormones naturally.
This doesn’t mean keto is a magic fix — it’s a supportive tool that, combined with lifestyle habits like sleep, stress management, and physical activity, can help you see measurable improvements over weeks.
Reduces Cravings and Stabilizes Energy
Do you notice mid-morning crashes or evening sugar cravings? Many women with PCOS experience blood sugar roller coasters, which make sticking to healthy habits tricky.
Keto’s higher fat and moderate protein intake can keep your energy more steady throughout the day. Paired with high-fiber, low-carb vegetables, this approach can quiet hunger signals and make portion control easier, helping you feel satisfied between meals.
May Improve Mood and Mental Clarity
Hormonal swings, insulin spikes, and erratic blood sugar can all affect mood, focus, and motivation. Some studies suggest that ketones, the energy molecules your body produces during ketosis, may provide a more stable fuel source for your brain, helping reduce brain fog and support focus.
While not everyone experiences the same effects, many women with PCOS report feeling mentally sharperand more balanced after a few weeks on a well-structured keto plan.
How to Tailor Your Keto Macros for PCOS
Not all ketogenic diets are created equal — and what works for your friend might not work for you. For women with PCOS, macro balance matters more than strict keto rules, because your hormones and insulin response can be very sensitive to carbohydrate and protein intake. This section will help you personalize your keto macros safely and effectively.
Why Macros Matter for PCOS
Macros — the percentages of carbs, protein, and fat in your diet — directly affect insulin levels, hormone balance, and energy. Too many carbs can spike insulin and worsen PCOS symptoms, while too much protein may convert to glucose in the body, also raising insulin.
A PCOS-focused keto plan usually emphasizes:
- Low-to-moderate carbs (20–50g/day, or slightly higher if active)
- Moderate protein (1–1.2g per kg body weight)
- Healthy fats (to meet energy needs and satiety)
Balancing macros helps maintain ketosis without triggering insulin surges or leaving you feeling deprived.
Calculating Your Carb Target
Most women with PCOS do well with a low-carb range tailored to their insulin sensitivity:
- 75–120g/day: For higher insulin resistance or weight loss focus
- 100–150g/day: Moderate approach for energy and hormonal balance
- 150–200g/day: For highly active women who need extra fuel
Spread your carbs across 3 meals + 1 snack, pairing them with protein and fiber to avoid blood sugar spikes. Non-starchy vegetables, berries, and small portions of low-GI fruits are ideal.
Setting Your Protein and Fat
- Protein: Aim for 20–30g per meal, roughly 1–1.2g/kg body weight per day. Protein helps control appetite, preserve muscle, and stabilize blood sugar.
- Fats: Fill the rest of your calories with healthy fats, like avocado, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. Fat provides sustained energy and supports hormone production.
Remember, the goal isn’t ultra-low carbs at all costs — it’s balance that supports your PCOS and daily life.
Tracking and Adjusting Macros
Everyone’s response to keto is different. Track your:
- Energy levels
- Hunger and cravings
- Weight, waist circumference, or body composition
- Menstrual cycle and PCOS symptoms
If you notice constant fatigue, cravings, or stalled results, adjust macros gradually: lower carbs 5–10g per day, shift carbs toward post-workout meals, or slightly increase protein for satiety.
Tip: Apps and food logs can help, but don’t obsess — listen to your body and tweak over 2–4 weeks.
Sample 7-Day PCOS Keto Meal Plan That Won’t Feel Restrictive + Free PDF Download
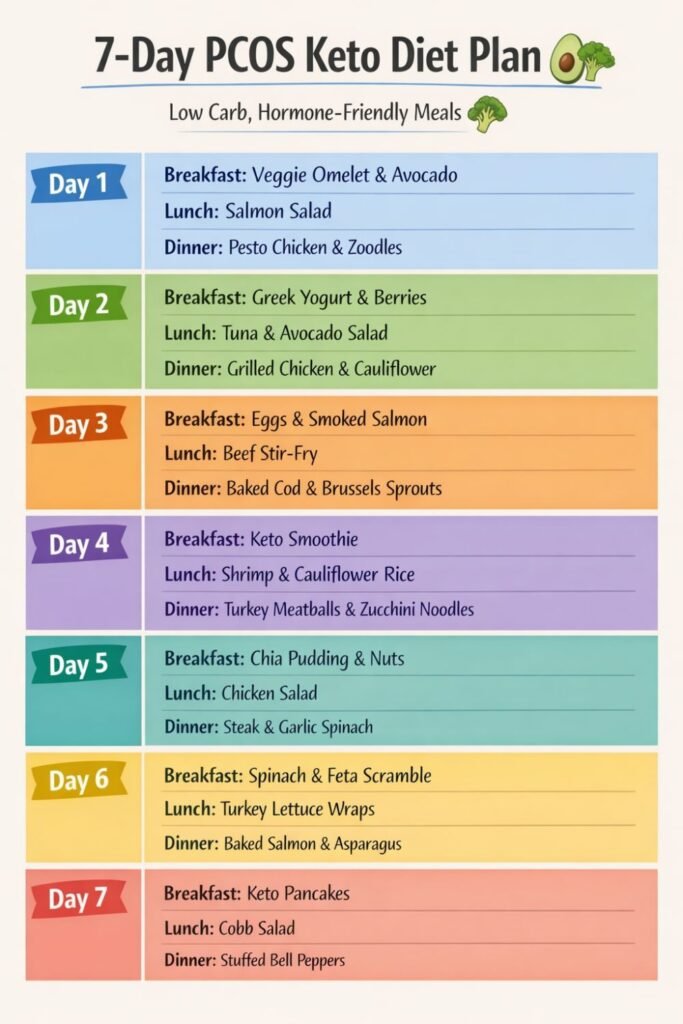
Eating keto with PCOS doesn’t mean you have to survive on eggs and bacon every day. The key is balance, variety, and flexibility. This 7-day plan focuses on low-carb, nutrient-dense foods, enough protein, healthy fats, and fiber to support hormone balance, energy, and satiety.
Tip: Adjust portions to your own calorie needs, activity level, and insulin response. Use this plan as a template rather than a strict rulebook.
Day 1
Breakfast: Veggie omelet with spinach, mushrooms, and feta + 1/4 avocado
Snack: 10 almonds + 1/2 cup blueberries
Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with leafy greens, olive oil, and pumpkin seeds
Snack: Celery sticks + 2 tbsp almond butter
Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted broccoli and cauliflower
Day 2
Breakfast: Greek yogurt (unsweetened) + chia seeds + small handful raspberries
Snack: 1 boiled egg + cucumber slices
Lunch: Zucchini noodles with shrimp and pesto
Snack: 1 oz cheese + a few walnuts
Dinner: Stir-fried tofu with green beans, sesame oil, and mushrooms
Day 3
Breakfast: Keto smoothie: unsweetened almond milk + spinach + protein powder + 1/2 avocado
Snack: 1 boiled egg + 1/4 cup sliced bell peppers
Lunch: Grilled turkey burger + side salad with olive oil vinaigrette
Snack: 10 macadamia nuts + 1/4 cup blueberries
Dinner: Roasted chicken thighs with sautéed zucchini and asparagus
Day 4
Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with smoked salmon + 1/4 avocado
Snack: Cucumber slices + guacamole
Lunch: Tuna salad with celery, mayo, and leafy greens
Snack: 1 boiled egg + handful of walnuts
Dinner: Beef stir-fry with broccoli, bell peppers, and coconut aminos
Day 5
Breakfast: Cottage cheese + chia seeds + small handful raspberries
Snack: 10 almonds + cucumber slices
Lunch: Grilled chicken Caesar salad (skip croutons, add extra olive oil)
Snack: 1 oz cheese + celery sticks
Dinner: Baked cod with roasted Brussels sprouts and olive oil drizzle
Day 6
Breakfast: Keto pancakes (almond flour) with 1/4 cup blueberries + 2 boiled eggs
Snack: 1/4 cup macadamia nuts + 1/2 cup strawberries
Lunch: Egg salad lettuce wraps
Snack: 1 boiled egg + sliced cucumber
Dinner: Grilled lamb chops + roasted cauliflower and spinach sauté
Day 7
Breakfast: Veggie frittata with zucchini, mushrooms, and feta
Snack: 1/4 avocado + 10 almonds
Lunch: Salmon salad with leafy greens, olive oil, and pumpkin seeds
Snack: 1 boiled egg + celery sticks
Dinner: Baked chicken breast + sautéed kale and roasted asparagus
Tips to Make It Feel Less Restrictive
- Swap freely: Replace proteins with your favorites (salmon ↔ chicken ↔ tofu).
- Add flavor: Use herbs, spices, and healthy oils liberally.
- Carb timing: If you exercise, place slightly more carbs around workouts.
- Hydrate & supplement: Drink water, and consider magnesium, potassium, or omega-3s if needed.
Hidden Traps: Common Keto Mistakes That Can Worsen PCOS Symptoms
Following a ketogenic diet can feel empowering for women with PCOS, but some subtle mistakes can actually backfire, impacting hormones, energy, and results. Let’s cover the traps that aren’t often mentioned and how to avoid them.
1. Overdoing Protein
It’s tempting to load up on protein, but too much can convert into glucose via a process called gluconeogenesis, which may raise insulin levels — counterproductive for PCOS.
Fix: Stick to moderate protein (about 1–1.2g per kg body weight), spread across meals, and pair it with healthy fats and fiber for satiety.
2. Neglecting Fiber
Many keto plans focus on meat, cheese, and fats, but low fiber intake can worsen constipation, bloating, and gut dysbiosis, all of which are linked to PCOS symptoms.
Fix: Include non-starchy vegetables, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and low-carb fruits to hit ~25–35g of fiber daily.
3. Ignoring Micronutrients
Restricting carbs can limit intake of essential vitamins and minerals like magnesium, potassium, vitamin D, and B-vitamins, which affect insulin sensitivity, mood, and energy.
Fix: Incorporate leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish, and consider supplementation after consulting your healthcare provider.
4. Skipping Meals or Under-Eating
Calorie restriction might seem like it speeds up results, but chronic under-eating can raise stress hormones like cortisol, which can worsen insulin resistance and hair loss.
Fix: Eat regular, balanced meals with protein, fiber, and healthy fats to stabilize hormones and energy levels.
5. Overemphasis on Weight Loss
Many women focus solely on scale numbers, but rapid weight loss can disrupt cycles and stress the body. PCOS isn’t just about losing pounds — it’s about hormonal balance and metabolic health.
Fix: Track energy, cravings, cycle regularity, and blood sugar trends in addition to weight.
6. Forgetting Lifestyle Factors
Keto alone isn’t a cure. Stress, poor sleep, and lack of movement can all counteract dietary benefits and worsen PCOS symptoms.
Fix: Prioritize 7–9 hours of sleep, gentle movement, and stress management techniques like meditation or deep breathing.
Quick Takeaway: Keto can be a powerful tool for PCOS, but ignoring these common mistakes can slow results or make symptoms worse. Personalization, balance, and awareness are key.
Lifestyle Tweaks to Boost Keto Results for PCOS
Eating keto can be powerful, but when combined with the right lifestyle habits, the benefits for women with PCOS can be dramatically amplified. Small tweaks can improve insulin sensitivity, hormone balance, and overall energy, making your keto plan more effective and sustainable.
1. Prioritize Sleep
Sleep isn’t just rest — it’s when your hormones, insulin sensitivity, and stress response reset. Poor sleep can spike cortisol, raise insulin, and worsen cravings, all of which make PCOS symptoms harder to manage.
Tip: Aim for 7–9 hours per night, keep a consistent schedule, and reduce screens 1 hour before bed. Even short naps can help if nighttime sleep is disrupted.
2. Manage Stress Effectively
Chronic stress increases cortisol and insulin, which can sabotage even the strictest keto plan. Mindfulness, yoga, deep breathing, or journaling can reduce stress and help balance hormones naturally.
Tip: Spend 5–10 minutes daily on stress-reduction exercises, and notice how your cravings and energy levels improve.
3. Incorporate Strength Training & Gentle Cardio
Exercise isn’t just about burning calories — it improves insulin sensitivity, lean muscle mass, and metabolic flexibility.
Tip:
- Strength training 2–3x/week (resistance bands, bodyweight, or weights)
- Gentle cardio 2–3x/week (walking, cycling, swimming)
- Avoid excessive high-intensity cardio, which can spike cortisol if overdone.
4. Stay Hydrated and Support Electrolytes
Keto can increase water loss, which may impact kidney function, energy, and digestion. Women with PCOS may be particularly sensitive to electrolyte imbalances.
Tip: Drink plenty of water, and include electrolyte-rich foods or supplements like magnesium, potassium, and sodium to prevent fatigue, cramps, and headaches.
5. Time Your Meals Thoughtfully
Meal timing can help stabilize insulin and energy levels. Front-loading protein and carbs earlier in the day can reduce afternoon crashes and evening cravings.
Tip: Spread your meals across 3–4 meals/snacks, and if you train, time slightly more carbs pre- or post-workout for energy and recovery.
6. Track Signals, Not Just Scale Numbers
The scale can be misleading. Instead, track energy levels, mood, menstrual cycle, cravings, and waist measurements to see how your body responds to keto and lifestyle changes.
Tip: Use a journal or app to log your meals, sleep, exercise, and symptoms. Adjust macros or lifestyle habits based on patterns, not perfection.
Quick Takeaway: Keto works best when paired with consistent sleep, stress management, strategic exercise, hydration, and mindful tracking. These small habits amplify results, keep hormones balanced, and make PCOS more manageable long-term.
Tracking Your Progress Safely: What to Measure and When
Following a keto plan for PCOS is exciting, but progress isn’t just about the scale. Tracking the right markers helps you see real improvements, adjust your plan wisely, and stay motivated — without stressing your hormones or obsessing over every pound.
1. Energy Levels and Cravings
Your daily energy and cravings are among the first signs your keto plan is working:
- Energy: Note how steady your energy is throughout the day. Are there crashes mid-morning or late afternoon?
- Cravings: Track sugar and carb cravings on a 0–10 scale. A drop in cravings usually means blood sugar and insulin are stabilizing.
Tip: Keep a simple journal or app log for 2–4 weeks before making big changes.
2. Menstrual Cycle Regularity
For women with PCOS, cycle changes reflect hormone balance. Keto, paired with lifestyle tweaks, may improve ovulation and cycle predictability:
- Track start/end dates, flow, and PMS symptoms.
- Note any improvements in cycle length and regularity, which indicate progress beyond weight loss.
3. Body Measurements
Weight alone can be misleading, especially if you’re gaining muscle while losing fat. Track:
- Waist circumference (abdominal fat is often more metabolically active)
- Hip/waist ratio
- Body composition (if available)
Even small improvements can signal hormonal and metabolic changes.
4. Blood Sugar and Insulin Signals
If you can, monitor markers of glucose and insulin:
- Fasting glucose and post-meal readings (optional: CGM)
- Fasting insulin or HOMA-IR values from your clinician
Tip: These measurements are optional but can confirm that your low-carb approach is improving insulin sensitivity.
5. Mood and Mental Clarity
PCOS and insulin resistance can affect mood, focus, and motivation. Track:
- Mood changes, irritability, or anxiety levels
- Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
- Sleep quality and restfulness
Improvement in these areas often signals your body is responding positively to keto.
6. How Often to Adjust
- Review progress every 2–4 weeks, not daily.
- Adjust macros gradually: ±5–10g carbs per meal or ±10–20g/day depending on energy, cravings, and menstrual health.
- Small tweaks over time are more sustainable than strict or rapid changes.
Quick Takeaway: Progress is multidimensional — energy, cravings, cycle, measurements, glucose, and mood all matter. Tracking safely ensures your keto plan supports long-term health, hormone balance, and PCOS management.
Conclusion
The journey with PCOS is unique for every woman, and there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. A ketogenic diet can be a powerful tool to improve insulin sensitivity, balance hormones, and support weight management, but its true success comes from personalization, consistency, and lifestyle integration.
By combining:
- Thoughtful macro tailoring
- A varied, nutrient-rich meal plan
- Awareness of common keto mistakes
- Supportive lifestyle habits
- Careful tracking of progress
…you give yourself the best chance to see meaningful, sustainable improvements — not just on the scale, but in energy, mood, menstrual cycles, and overall health.
Remember: Keto isn’t about perfection — it’s about finding a balanced approach that works for your body and your life. Use this plan as a guideline, not a strict rule, and adjust based on how you feel, what your data shows, and your clinician’s advice.
With patience, consistency, and awareness, a PCOS Keto Diet Plan can become a practical, empowering strategy to reclaim your energy, stabilize hormones, and feel like yourself again.
References
Mavropoulos, J. C., Yancy, W. S., & Westman, E. C. (2005). The effects of a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet on the polycystic ovary syndrome: A pilot study. Nutrition & Metabolism, 2, 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-2-35
Cannarella, R., Rubulotta, M., & Leonardi, A. (2025). Effects of ketogenic diets on polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 23, 74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-025-01411-1
Khalid, K., Apparow, S., & Mushaddik, I. L. (2023). Effects of ketogenic diet on reproductive hormones in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Journal of the Endocrine Society, 7(10), bvad112. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2023-03332
Gonzalez, F., & Rote, N. S. (2014). Polycystic ovary syndrome and type 2 diabetes: The metabolic syndrome of the ovary. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 99(2), 1144-1152. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-3332
Sharma, S., Sood, A., & Sood, R. (2020). Effects of a ketogenic diet on weight, insulin sensitivity, and reproductive hormones in women with PCOS: A systematic review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(11), 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113677